TDS Meters:
-
TDS meter is used to measure the total disolved solids in water. TDS value helps to determine if it's the time to change RO membrane, not for replacement filters. Replacement filters should be changed periodically to protect the RO membrane.
-
Be careful the fake TDS-3 Meter sold online: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Y3bzNy9i214
-
TDS-MINI: $25 [Out of Stock]
-
TDS-3: $35
-
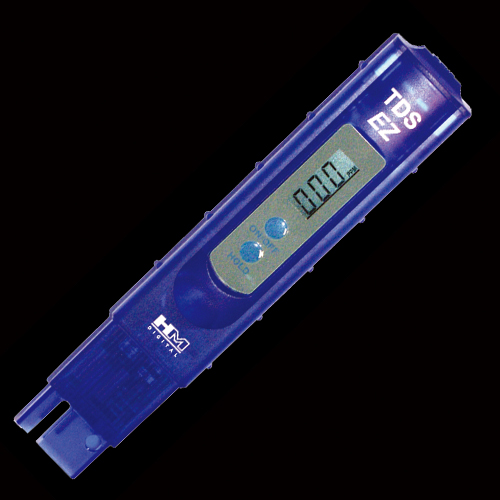
TDS-EZ: $30 [Out of Stock]
-
PH-200: $75 [Out of Stock]
What is TDS (Total Dissolved Solids)? Where does it come from, why is it important and how to treat it?
Total Dissolved Solids (TDS) are the total weight of all solids that are dissolved in a given volume of water, expressed in units of mg per unit volume of water (mg/L), also referred to as parts per million (PPM).
Questions and Answers about TDS in your water:
What are Total Dissolved Solids?
Where do Dissolved Solids come from?
Why should you measure the TDS levels in your water?
How do you reduce or remove the TDS in your water?
How do I check Reverse Osmosis membrane performance with this TDS meter?
1. "Dissolved solids" refer to any minerals, salts, metals, cations or anions dissolved in water. This includes anything present in water other than the pure water (H20) molecule and suspended solids. (Suspended solids are any particles/substances that are neither dissolved nor settled in the water, such as wood pulp.)
2. In general, the total dissolved solids concentration is the sum of the cations (positively charged) and anions (negatively charged) ions in the water.
3. Parts per Million (ppm) is the weight-to-weight ratio of any ion to water.
4. Conductivity is usually about 100 times the total cations or anions expressed as equivalents. Total dissolved solids (TDS) in ppm usually ranges from 0.5 to 1.0 times the electrical conductivity.
1. Some dissolved solids come from organic sources such as leaves, silt, plankton, and industrial waste and sewage. Other sources come from runoff from urban areas, road salts used on street during the winter, and fertilizers and pesticides used on lawns and farms.
2. Dissolved solids also come from inorganic materials such as rocks and air that may contain calcium bicarbonate, nitrogen, iron phosphorous, sulfur, and other minerals. Many of these materials form salts, which are compounds that contain both a metal and a nonmetal. Salts usually dissolve in water forming ions. Ions are particles that have a positive or negative charge.
3. Water may also pick up metals such as lead or copper as they travel through pipes used to distribute water to consumers.
The EPA Secondary Regulations advise a maximum contamination level (MCL) of 500mg/liter (500 parts per million (ppm) for TDS. Numerous water supplies exceed this level. When TDS levels exceed 1000mg/L it is generally considered unfit for human consumption. A high level of TDS is an indicator of potential concerns, and warrants further investigation. Most often, high levels of TDS are caused by the presence of potassium, chlorides and sodium. These ions have little or no short-term effects, but toxic ions (lead arsenic, cadmium, nitrate and others) may also be dissolved in the water.
The following are reasons why it is helpful to constantly test for TDS:
| Taste/Health | High TDS results in undesirable taste which could be salty, bitter, or metallic. It could also indicate the presence of toxic minerals. The EPA's recommended maximum of TDS in water is 500mg/L (500ppm). |
| Filter performance | Test your water to make sure the filter system has a high rejection rate and know when to change your filter (or membrane) cartridges. |
| Hardness | High TDS indicates Hard water, which causes scale buildup in pipes and valves, inhibiting performance. |
| Aquaculture | A constant level of minerals is necessary for aquatic life. The water in an aquarium should have the same levels of TDS and pH as the fish and reef's original habitat. |
| Hydroponics | TDS is the best measurement of the nutrient concentration in a hydroponics' solution. |
| Pools and Spas | TDS levels must be monitored to prevent maintenance problems. |
| Commercial/Industrial | High TDS levels could impede the functions of certain applications. |
1. Carbon Filters (very slight reduction)
2. Reverse Osmosis (RO) (extremely high reduction and great tasting water )
3. Distillation (total reduction - flat taste)
4. DI Deionization (usually a final polishing filter following a RO Reverse Osmosis filtration system to eliminate TDS)
Example:
1. TDS of incoming water (before entering RO filter): 500ppm; TDS of RO water: 25ppm
2. Percent of rejection: 1 - (25 / 500) = 0.95 or 95%
3. If this number is less than 85%, it's time to replace the RO membrane.
#15